Importing the workshop files into the JupyterLab environment
The JupyterLab environment is web-based, but all operations run on Red Hat OpenShift AI and are backed by the OpenShift cluster. This configuration allows you to run notebooks without installing local tools or consuming local CPU, GPU, or memory resources.
You created a workbench, as described in Creating a workbench and selecting a workbench image.
-
In the Workbenches tab for your project, click the link for your workbench. If prompted, log in and allow JupyterLab to authorize your user.
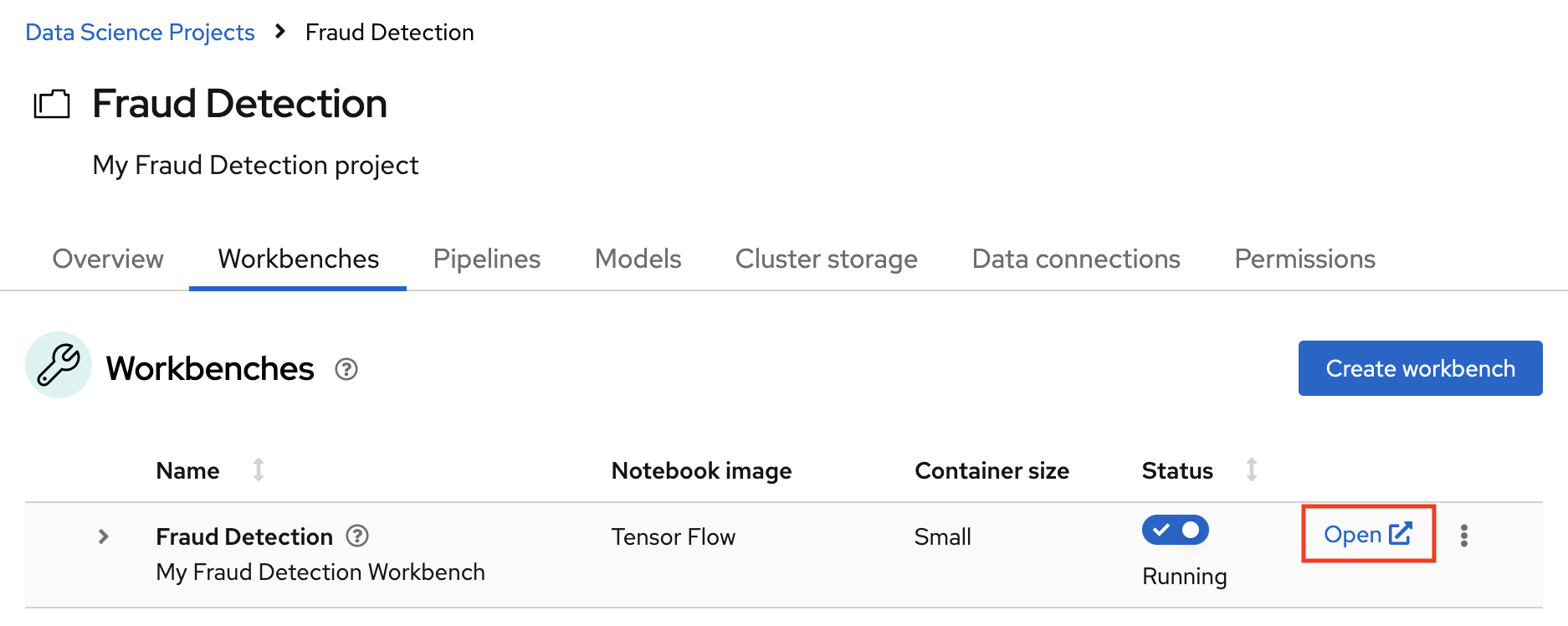
Your JupyterLab environment window opens.
This file-browser window shows the files and folders that are saved inside your own personal space in OpenShift AI.
-
Bring the content of this workshop inside your JupyterLab environment:
-
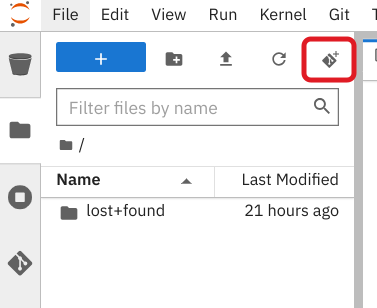
On the toolbar, click the Git Clone icon:
-
Enter the following workshop Git https URL:
https://github.com/rh-aiservices-bu/fraud-detection.git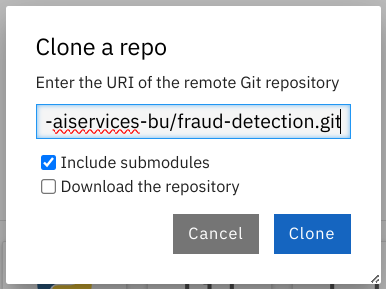
-
Select the Include submodules option, and then click Clone.
-
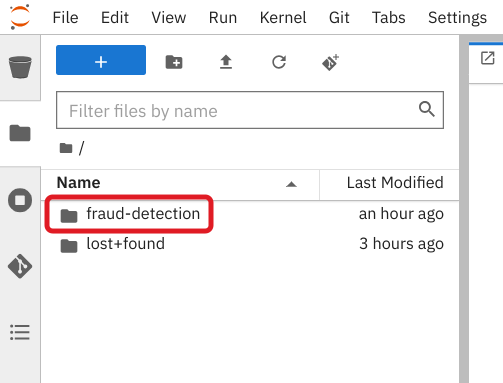
In the file browser, double-click the newly-created fraud-detection folder to expand its contents.
-
In the left navigation bar, click the Git icon, and then click Current Branch to expand the branches and tags selector panel.
-
On the Branches tab, in the Filter field, enter main.
-
-
Select origin/main.
The current branch changes to main.
-
-
In the left navigation bar, click the file browser icon to view the notebooks that you cloned from Git.
-
Verify that the Git version at the bottom of the JupyterLab window is main.
or